All-in-One Molecular AIE Theranostics: Fluorescence Image Guidedand Mitochondria Targeted Chemo- and Photodynamic Cancer CellAblation
Abstract
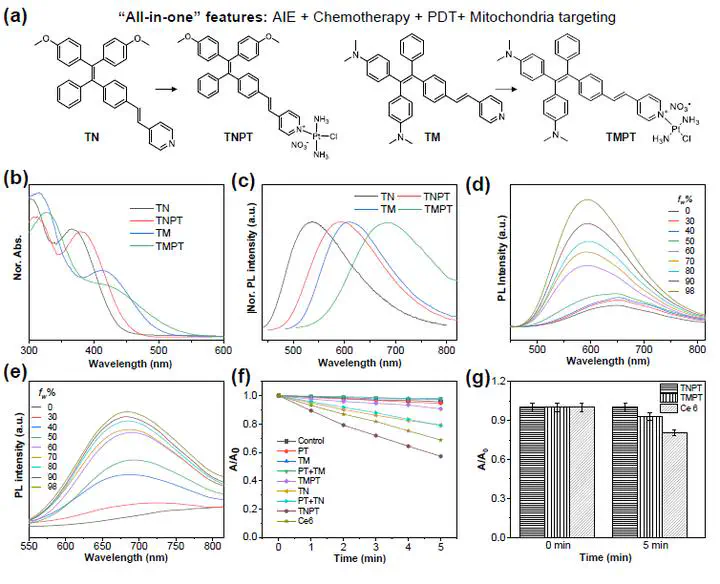
Molecular theranostic platforms with precise molecular structure and multiple functions hold great promise for cancer therapy. Different from current strategy to incorporate various components into single entities with the risk of compromised efficacy and poor reproducibility, herein, molecular aggregation-induced-emission (AIE) photosensitizers with ingenious integration of AIE fluorophore and cisplatin are facilely synthesized for synergetic anticancer therapy. Through adjusting donor structures coordinated with cisplatin moiety and balancing the hydrophobic-hydrophilic prop-erty, donor-acceptor strength, and intramolecular charge transfer effect, the newly designed AIE photosensitizer TNPT exhibits good cellular uptake with predominant mitochondria location of cancerous cells, high chemotherapeutic efficacy similar to cisplatin, and strong reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation capability better than chlorin e6 (Ce6). Im-portantly, TNPT demonstrates synergetic photodynamic and chemo-therapy on C6 glioma cells, showing 2.4-fold more potent than cisplatin upon white light irradiation (15 J/cm2). Further cell cycle analysis and apoptosis assay indicate that the photodynamic and chemo-therapeutic functions of TNPT synergistically inhibit DNA replication and cause cell apop-tosis. In addition, TNPT exhibits selective uptake on cancerous cells rather than normal cells, contributing to significantly lower cytotoxicity to normal cells as compared to free cisplatin. This study provides a facile strategy to design molecular theranostic agents.